给定半径圆覆盖点
2013-08-06 算法 算法 计算几何 487 字 1 分钟
给定一个圆,使其能覆盖平面上最多的点。
题目模型
给平面上N个点的坐标 ( Xi,Yi ),给出圆半径 R ,求 R 能覆盖的最多的点数。
题目分析
最初的分析就是移动,保证点在圆周上,然后圆以这一点为轴转动360度,检查有多少个点能被圆覆盖。操作时,对于基点 i ,如果 dist(i, j)<D 那么就以i点为轴转动圆周到 j 在圆周上。但是这么做的正确性没有仔细想过,但是实现起来就相当麻烦了。时间复杂度上是 O(N^2) 肯定是可以接受的。这种想法还有待于更深入的讨论。
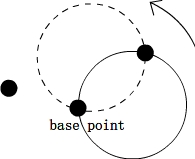 后来在网上发现一种做法,就是以每个点为圆心,以半径R画圆,然后统计每个区域重叠的次数,记录最大。
后来在网上发现一种做法,就是以每个点为圆心,以半径R画圆,然后统计每个区域重叠的次数,记录最大。
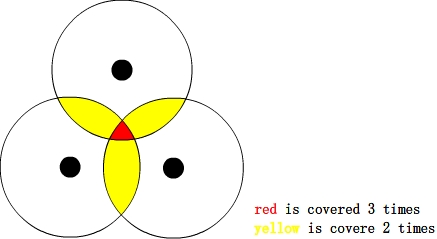 但是,如果要表示一个区域,是几乎不可能的事情。区域是不规则的,最初我想将区域栅格化,但是时间复杂度和正确性上都是不能保证的。最后还是看了报告……
仔细观察上图,虽然红色区域不能被表示,但是围成区域的边界却是能表示的。由于边界是圆弧,所以可以用这段弧对于x轴的极角表示,
但是,如果要表示一个区域,是几乎不可能的事情。区域是不规则的,最初我想将区域栅格化,但是时间复杂度和正确性上都是不能保证的。最后还是看了报告……
仔细观察上图,虽然红色区域不能被表示,但是围成区域的边界却是能表示的。由于边界是圆弧,所以可以用这段弧对于x轴的极角表示,
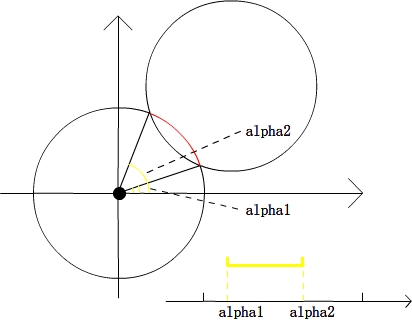 区域问题转化成了线段覆盖次数的问题了。然后就是把alpha1,alpha2映射到一个[0, 4pi]的区间,这里映射到[0, 4pi]而不是[0, 2pi]是由于alpha的范围是[-pi/2, 5pi/2],而非[0, 2pi],对于不在[0,4pi]范围内的点,直接加2pi不会影响结果。
区域问题转化成了线段覆盖次数的问题了。然后就是把alpha1,alpha2映射到一个[0, 4pi]的区间,这里映射到[0, 4pi]而不是[0, 2pi]是由于alpha的范围是[-pi/2, 5pi/2],而非[0, 2pi],对于不在[0,4pi]范围内的点,直接加2pi不会影响结果。
这里再说明一下这种方法:
首先将重叠的弧的开始点和结束点标示出来(如开始点为 1 ,结束点为 0),那么将弧按极角排序之后,遇到开始点的时候计数器加 1 ,遇到结束点计数器减 1。统计这个期间计数器的最大值就是圆重叠的最大数。具体原理可以参考一下上面的图片。
例题
hoj2704 Phone Cell
直接套用算法就可以解决。
题目连接:http://acm.hit.edu.cn/hoj/problem/view?id=2704
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const double pi = acos(-1);
const int MAXN = 2048;
struct point
{
double x, y;
};
point list[MAXN];
struct interval
{
double arg;
bool flag;
bool operator<(const interval &T) const
{
return arg < T.arg;
}
};
interval event[4 * MAXN];
double dis(point a, point b)
{
return sqrt((a.x - b.x)*(a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y)*(a.y - b.y));
}
int main()
{
int n;
int num, res, ans;
double r;
double dist, a1, a2, delta, cta;
while(scanf("%d%lf", &n, &r) && n)
{
r += 0.01;
ans = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%lf%lf", &list[i].x, &list[i].y);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
num = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if(i == j) continue;
dist = dis(list[i], list[j]);
if(dist <= 2.0 * r)
{
cta = atan2(list[j].y - list[i].y, list[j].x - list[i].x);
if(cta < 0) cta += 2 * pi;
delta = acos(dist / 2.0 / r);
a1 = cta - delta, a2 = cta + delta;
if(a1 < 0)
{
event[num].arg = a1 + 2 * pi, event[num++].flag = true;
event[num].arg = a2 + 2 * pi, event[num++].flag = false;
}
else
{
event[num].arg = a1, event[num++].flag = true;
event[num].arg = a2, event[num++].flag = false;
event[num].arg = a1 + 2 * pi, event[num++].flag = true;
event[num].arg = a2 + 2 * pi, event[num++].flag = false;
}
}
}
if(num < ans) continue;
sort(event, event + num);
res = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < num; j++)
{
if(event[j].flag) res++;
else res--;
if(ans < res) ans = res;
}
}
if(ans != -1) printf("It is possible to cover %d points.\n", ans + 1);
else printf("It is possible to cover 1 points.\n");
}
return 0;
}
hoj1799 Circle and Points
这个问题与上一个问题类似,只不过半径固定为 1.0 。其它的没什么特殊的地方。
题目链接:http://acm.hit.edu.cn/hoj/problem/view?id=1799
hoj2940 Pit Lord
这个问题每个点都有一个权值,可以考虑“进入”的时候增加的是点的权值,而“离开”的时候减去点的权值。
题目链接:http://acm.hit.edu.cn/hoj/problem/view?id=2940
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct point
{
double x,y;
double val;
void read()
{
cin>>x>>y>>val;
}
}p[1005];
struct node
{
double dius;
int flag;
double val;
};
int n;
double r;
double ans;
vector<node>lists;
double dis(point a,point b)
{
return(sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)));
}
int cmp(node a,node b)
{
return(a.dius<b.dius);
}
int main()
{
while(cin>>n>>r)
{
r+=0.001;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
p[i].read();
}
ans=0.0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
lists.clear();
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(i==j) continue;
double dist=dis(p[i],p[j]);
if(dist<=2.0*r)
{
double cta=atan2(p[j].y-p[i].y,p[j].x-p[i].x);
if(cta<0) cta+=2.0*M_PI;
double delta=acos(dist/2.0/r);
double a1=cta-delta,a2=cta+delta;
node tmp;
if(a1<0)
{
tmp.dius=a1+2.0*M_PI;tmp.flag=1;tmp.val=p[j].val;
lists.push_back(tmp);
tmp.dius=a2+2.0*M_PI;tmp.flag=0;tmp.val=p[j].val;
lists.push_back(tmp);
}
else
{
tmp.dius=a1;tmp.flag=1;tmp.val=p[j].val;
lists.push_back(tmp);
tmp.dius=a2;tmp.flag=0;tmp.val=p[j].val;
lists.push_back(tmp);
tmp.dius=a1+2.0*M_PI;tmp.flag=1;tmp.val=p[j].val;
lists.push_back(tmp);
tmp.dius=a2+2.0*M_PI;tmp.flag=0;tmp.val=p[j].val;
lists.push_back(tmp);
}
}
}
sort(lists.begin(),lists.end(),cmp);
double res=0;
for(int k=0;k<lists.size();k++)
{
if(lists[k].flag)
{
res+=lists[k].val;
}
else
{
res-=lists[k].val;
}
if(res+p[i].val>ans) ans=res+p[i].val;
}
}
printf("%.2lf\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
ural1332 Genie Bomber
这个问题的特殊之处就在于每个点也有自己的半径,也就是用大圆 R 来覆盖若干小圆 r 。这里的处理方法是将 R-r 作为覆盖圆来使用。注意 R-r 为负值的时候要输出 0 。
题目链接:http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=1332
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct point
{
double x,y;
void read()
{
cin>>x>>y;
}
}p[305];
struct node
{
double dius;
int flag;
};
vector<node>lists;
double dis(point a,point b)
{
return(sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)));
}
int cmp(node a,node b)
{
return a.dius<b.dius;
}
int ans=0;
double R,r;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
p[i].read();
}
cin>>R>>r;
R-=r;
if(R<0)
{
cout<<"0"<<endl;
return 0;
}
ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
lists.clear();
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(i==j) continue;
double dist=dis(p[i],p[j]);
if(dist<=2.0*R)
{
double cta=atan2(p[j].y-p[i].y,p[j].x-p[i].x);
if(cta<0) cta+=2.0*M_PI;
double delta=acos(dist/2.0/R);
double a1=cta-delta,a2=cta+delta;
node tmp;
if(a1<0)
{
tmp.dius=a1+2.0*M_PI;tmp.flag=1;
lists.push_back(tmp);
tmp.dius=a2+2.0*M_PI;tmp.flag=0;
lists.push_back(tmp);
}
else
{
tmp.dius=a1;tmp.flag=1;
lists.push_back(tmp);
tmp.dius=a2;tmp.flag=0;
lists.push_back(tmp);
tmp.dius=a1+2.0*M_PI;tmp.flag=1;
lists.push_back(tmp);
tmp.dius=a2+2.0*M_PI;tmp.flag=0;
lists.push_back(tmp);
}
}
}
sort(lists.begin(),lists.end(),cmp);
int cnt=0;
for(int k=0;k<lists.size();k++)
{
if(lists[k].flag) cnt++;
else cnt--;
if(cnt>ans) ans=cnt;
}
}
cout<<ans+1<<endl;
return 0;
}
参考内容
后来在网上发现一种做法,就是以每个点为圆心,以半径R画圆,然后统计每个区域重叠的次数,记录最大。
但是,如果要表示一个区域,是几乎不可能的事情。区域是不规则的,最初我想将区域栅格化,但是时间复杂度和正确性上都是不能保证的。最后还是看了报告…… 仔细观察上图,虽然红色区域不能被表示,但是围成区域的边界却是能表示的。由于边界是圆弧,所以可以用这段弧对于x轴的极角表示,
区域问题转化成了线段覆盖次数的问题了。然后就是把alpha1,alpha2映射到一个[0, 4pi]的区间,这里映射到[0, 4pi]而不是[0, 2pi]是由于alpha的范围是[-pi/2, 5pi/2],而非[0, 2pi],对于不在[0,4pi]范围内的点,直接加2pi不会影响结果。